Difference Between Supercharger and Turbocharger
The first difference between the super and turbo charger is that of the prime mover. The supercharger draws its energy from a compressor, which is an auxiliary of the engine itself. The turbocharger however derives its power from the exhaust gases coming out of the engine. Thus the performance of the engine is enhanced without disturbing its normal operation and rpm’s.
This difference also dictates the applications in which these chargers can be used. In applications where fuel economy has a priority over the compression ratio (and thus the speed), turbochargers are used, for example, in the automobiles. In the applications where performance matters more than the fuel economy, for example formula one race cars, superchargers are used.
The power output of the superchargers is easier to control. The turbochargers rely on the exhaust gases, which can vary in pressure and are at extremely high temperatures. Thus when higher power output is required, the control can become pretty difficult and there is a delay called ‘turbo lag’. The reliance on the exhaust gases means that there will a small delay between the opening of the throttle valve and the impingement of the gases on the turbine blade. In case of superchargers (belt or gear driven) though, the variation in power is instantaneous.
When it comes to compactness, turbocharger takes the lead. As compared to a supercharger, it is a small device and can be easily accommodated. The superchargers are also more expensive than the turbochargers.
Both super and turbochargers require intercoolers to reduce the temperature of the gases, thus reducing the specific volume and making the combustion process more efficient.
Instructions
-
1
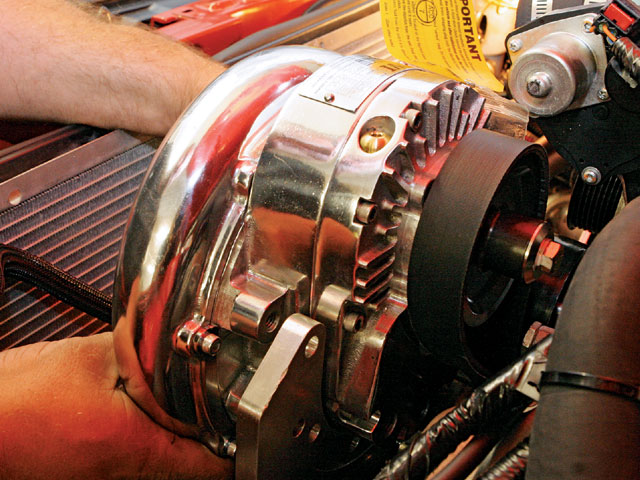
Supercharger
The purpose of the supercharger is to increase the compression ratio of the air before it enters the engine for combustion. In a supercharger, the compressor used to increase this ratio, is driven by the engine itself, thus decreasing the overall efficiency, for the same fuel consumption levels, as compared to a turbocharger. Its output is however steady and can be significantly increased by increasing the fuel consumption.
Image courtesy: howstuffworks.com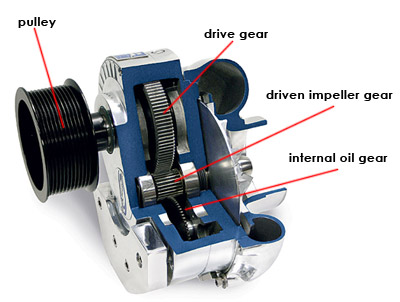
-
2
Turbocharger
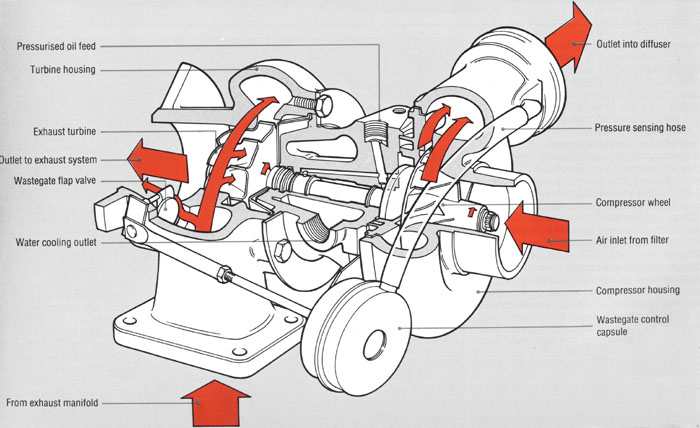
A turbocharger is a device which used the exhaust gases to drive a compressor and help the engine produce more power from the same displacement. The operation of the turbocharger depends on the pressure and temperature of the exhaust gases. These gases operate a compressor which increases the pressure of the air about to enter the engine, thus increasing the efficiency.
Image courtesy: rricketts.com